
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is a Title Loan?
- What Makes It a “Discount” Title Loan?
- How Title Loans Work
- Eligibility Requirements
- Pros and Cons of Discount Title Loans
- Title Loans vs. Payday Loans
- Interest Rates and Fees Explained
- Risks Involved
- State Regulations You Should Know
- Alternatives to Discount Title Loans
- How to Find Reputable Lenders
- Real-Life Scenarios: When a Title Loan Might Make Sense
- Tips to Pay Off a Title Loan Faster
- Final Thoughts
- FAQs
1. Introduction
In times of financial stress, some people turn to quick-fix lending solutions such as title loans. Among these, a “discount title loan” might sound like a more affordable version—but what does that really mean? Are you getting a deal, or just dressing up a high-risk loan in a friendlier name?
This guide explores everything you need to know about discount title loans, including how they work, their pros and cons, legal implications, and alternatives.
2. What Is a Title Loan?
A title loan is a secured loan where you use your vehicle title as collateral. In simple terms, you’re borrowing money and putting up your car, motorcycle, or truck as security. If you fail to repay the loan, the lender has the right to take your vehicle.
Key Characteristics:
- Short-term loan (usually 15 to 30 days)
- Loan amounts typically range from $100 to $10,000
- No credit check required
- Lender places a lien on your car title
3. What Makes It a “Discount” Title Loan?
A discount title loan usually implies:
- Lower interest rates than traditional title loans
- Waived or reduced processing fees
- Deferred or forgiven interest for early repayment
- Promotional offers (like first 30 days interest-free)
However, these “discounts” often come with strings attached—such as specific repayment dates or higher penalties if missed.
4. How Title Loans Work
Let’s break down the typical process:
- Application: You apply online or at a storefront, providing ID, income proof, and your car title.
- Vehicle Inspection: The lender assesses your vehicle’s value.
- Loan Approval: You’re offered a loan—usually up to 25% to 50% of your car’s value.
- Lien Registration: The lender places a lien on your title.
- Funding: Money is disbursed within 30 to 60 minutes.
- Repayment: You repay in lump sum or installments, depending on the terms.
5. Eligibility Requirements
To qualify for a discount title loan, you typically need:
- A vehicle with a clear title (no existing liens)
- Government-issued ID
- Proof of income (paystubs, benefits, etc.)
- Proof of residence
- Vehicle insurance (sometimes required)
- Must be 18 or older
Some lenders may offer discounted rates if you’re a veteran, student, or returning customer.
6. Pros and Cons of Discount Title Loans
✅ Pros:
- Fast approval & funding
- No credit check
- Possible lower interest rates
- Use of vehicle during loan term
❌ Cons:
- Risk of losing your vehicle
- Short repayment window
- High APR even with “discounts”
- Can trap you in a debt cycle
Important Note: Even “discount” versions of title loans often carry APR rates from 100% to 300% or more.
7. Title Loans vs. Payday Loans
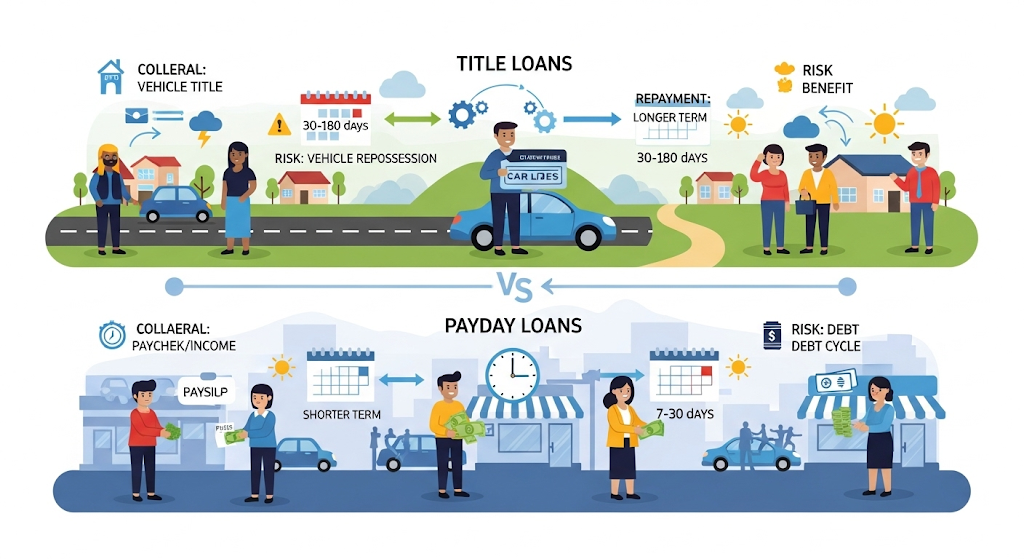
| Feature | Title Loan | Payday Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Collateral | Yes (car title) | No |
| Loan Amount | $100 to $10,000 | $50 to $1,000 |
| Credit Check | Not required | Not required |
| Interest Rate | High (100–300% APR) | Very High (300–600% APR) |
| Risk | Vehicle repossession | Account overdraft |
While both are expensive, title loans are secured and typically allow for larger loan amounts.
8. Interest Rates and Fees Explained
Even a “discount” title loan may charge:
- Monthly interest rate: Often 20–30%
- Annual Percentage Rate (APR): 240–360% or more
- Processing Fee: $25–100
- Late Fees: Flat fee or % of missed payment
- Lien Fee: Charged for placing a lien on your title
Example:
A $1,000 loan with a 25% monthly interest rate would cost $250/month, excluding other fees.
9. Risks Involved
- Repossession: Miss a payment and your car could be taken—often without warning.
- Debt Trap: Many borrowers “roll over” the loan, adding more fees and interest.
- Aggressive Collection Tactics: Lenders may call employers, family, or tow your car without notice.
- Credit Impact: While not reported to credit bureaus, unpaid loans could go to collections.
10. State Regulations You Should Know
Title loans are regulated at the state level. Some states ban them outright (e.g., New York, Massachusetts, Maryland), while others have strict rules.
States Where Title Loans Are Banned:
- New York
- New Jersey
- Massachusetts
- Pennsylvania
States With Interest Rate Caps:
- Illinois: Max 36% APR
- California: Max $7,500 loan with interest cap
- Florida: 30% for first $2,000, 24% next $1,000, 18% above that
Always check your state’s Department of Financial Institutions (DFI) for updated laws.
11. Alternatives to Discount Title Loans
Before choosing a title loan, consider these safer alternatives:
- Credit Union Personal Loans: Often offer low rates with flexible terms
- Paycheck Advance from Employer
- Family or Friends
- 0% APR Credit Cards (if eligible)
- Local Charities or Nonprofits: May help with utilities, food, or short-term loans
- Buy Now, Pay Later Plans (for purchases)
12. How to Find Reputable Lenders
Use the following checklist:
✅ Licensed in your state
✅ Transparent about fees and APR
✅ No hidden prepayment penalties
✅ Online reviews and Better Business Bureau (BBB) rating
✅ Offers written contracts and receipts
Avoid lenders who:
- Demand upfront fees
- Refuse to provide documents
- Pressure you to take more than needed
13. Real-Life Scenarios: When a Title Loan Might Make Sense
While risky, a discount title loan might be an option if:
- You need cash same day for an emergency (like medical bills or eviction)
- You own your car outright
- You’ve exhausted other borrowing options
- You can repay quickly, ideally within 15–30 days
In such cases, opt for lenders offering early repayment incentives.
14. Tips to Pay Off a Title Loan Faster
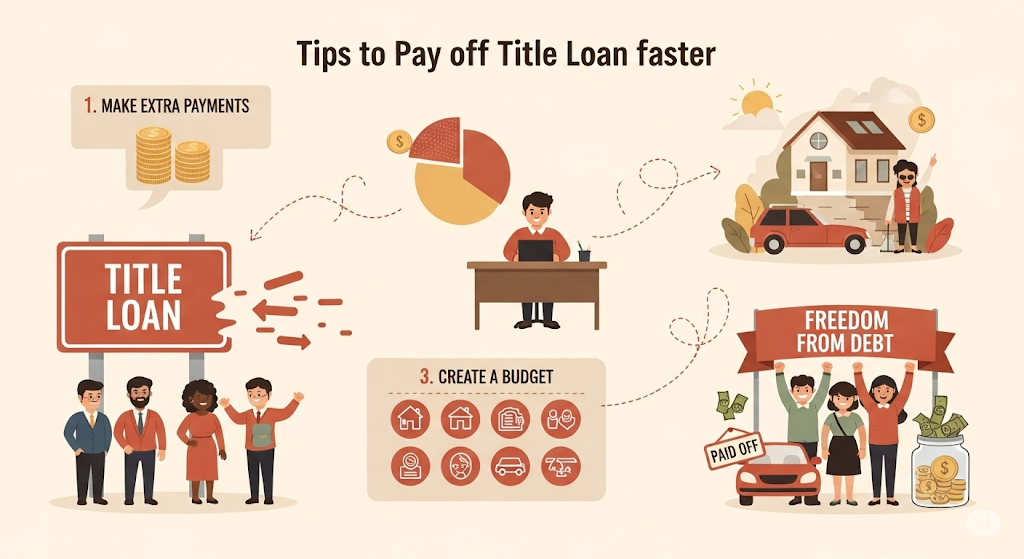
- Round Up Your EMIs: Pay more than minimum
- Biweekly Payments: Cut your term in half
- Use Tax Refund or Bonus: Pay down in lump sum
- Avoid Rollovers: They add fees and extend debt
- Ask for Discounts: Some lenders waive final payment fees if paid early
15. Final Thoughts
Discount title loans are not always the bargain they appear to be. Even with lower rates or waived fees, they remain high-risk, high-interest loans that can lead to vehicle loss or financial instability. Only use one as a last resort, and make sure you understand the terms, risks, and your ability to repay on time.
Better yet, explore safer borrowing alternatives like personal loans from credit unions, borrowing from friends or family, or emergency aid from nonprofits.
16. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Are discount title loans really cheaper?
Not necessarily. “Discount” often refers to reduced interest or fees for a limited period.
Q2: Can I still use my car during the loan term?
Yes, unless you default on the loan.
Q3: Do title loans affect my credit score?
Usually not—unless the loan is sent to collections.
Q4: What happens if I can’t repay?
You risk repossession of your vehicle and added late fees.
Q5: Can I get a title loan without a job?
Possibly, if you have other income sources like benefits or a co-signer.
Q6: Can I renew or extend a title loan?
Some lenders allow rollovers, but they add cost and risk.
Q7: Is a co-signer allowed for a title loan?
Usually not needed, but some lenders accept co-signers for better terms.
Q8: How do I know if a lender is legit?
Check licensing, read online reviews, and look for complaints with your state DFI.
Q9: Are online title loans safe?
Only if the lender is licensed and has a secure platform.
Q10: Can I negotiate the loan terms?
Yes, especially on repayment terms and prepayment penalties.




