Is a Student Loan Secured or Unsecured?
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is a Student Loan?
- Secured vs. Unsecured Loans: The Basics
- Are Student Loans Secured or Unsecured?
- Why Most Student Loans Are Unsecured
- What Happens If You Default on a Student Loan?
- Private vs. Federal Student Loans
- How Lenders Recover Money Without Collateral
- Are There Any Secured Student Loans?
- Impact of Unsecured Loans on Your Credit
- Can You Get a Secured Student Loan in the USA?
- Pros and Cons of Unsecured Student Loans
- Student Loan Forgiveness & Repayment Plans
- Tips to Manage Unsecured Student Loans
- Conclusion
- FAQs
1. Introduction
Student loans help millions of students pursue higher education. But one common question many borrowers ask is: Are student loans secured or unsecured?
The answer can affect how lenders view risk, what happens if you default, and even your financial planning after graduation.
This blog breaks down everything you need to know about student loan security, including legal implications, differences between loan types, and why it matters for borrowers and lenders alike.
2. What Is a Student Loan?
A student loan is a financial product designed to help students pay for post-secondary education and associated fees like tuition, books, and living expenses.
These loans are usually offered by:
- Federal Government (e.g., Direct Subsidized/Unsubsidized Loans)
- Private Lenders (e.g., banks, credit unions)
Student loans often come with special terms such as:
- Deferred payments while in school
- Lower interest rates
- Income-driven repayment options
3. Secured vs. Unsecured Loans: The Basics
Before answering the main question, let’s clarify two essential concepts:
🔒 Secured Loans
These loans are backed by collateral—something valuable like a car, house, or savings account. If the borrower doesn’t repay the loan, the lender can seize the asset.
Examples:
- Home mortgage (collateral: house)
- Auto loan (collateral: car)
- Gold loan (collateral: gold/jewelry)
🔓 Unsecured Loans
These are not backed by any asset. The lender relies on the borrower’s creditworthiness and promise to repay. If the borrower defaults, the lender cannot seize property but can take legal action or report the default to credit bureaus.
Examples:
- Credit cards
- Personal loans
- Most student loans
4. Are Student Loans Secured or Unsecured?
Most student loans in the USA are unsecured.
This means:
- You do not need to provide any collateral to borrow.
- The loan is granted based on your or your co-signer’s creditworthiness.
- You are still legally required to repay the debt, even if you declare bankruptcy (in most cases).
So Why Are They Called “Unsecured”?
Because no asset (like a house, car, or savings) is tied directly to the loan. If you don’t repay, the lender can’t take away a physical asset—but the consequences are still serious.
5. Why Most Student Loans Are Unsecured
Here are key reasons:
- Students typically don’t have major assets to pledge as collateral.
- The goal is to expand access to education, not restrict it.
- Government-backed loans are designed to promote higher education and reduce financial barriers.
- Lenders recover money through income-based repayment and legal enforcement—not asset seizure.
6. What Happens If You Default on a Student Loan?
Just because student loans are unsecured doesn’t mean you’re safe from penalties.
Consequences of Default:
- Damage to your credit score
- Collection agencies may get involved
- Wage garnishment
- Tax refund offset
- Ineligibility for future federal aid
- Potential legal action
Note: Unlike many other unsecured loans, student loans are rarely discharged in bankruptcy. You must show “undue hardship,” which is extremely hard to prove in court.
7. Private vs. Federal Student Loans
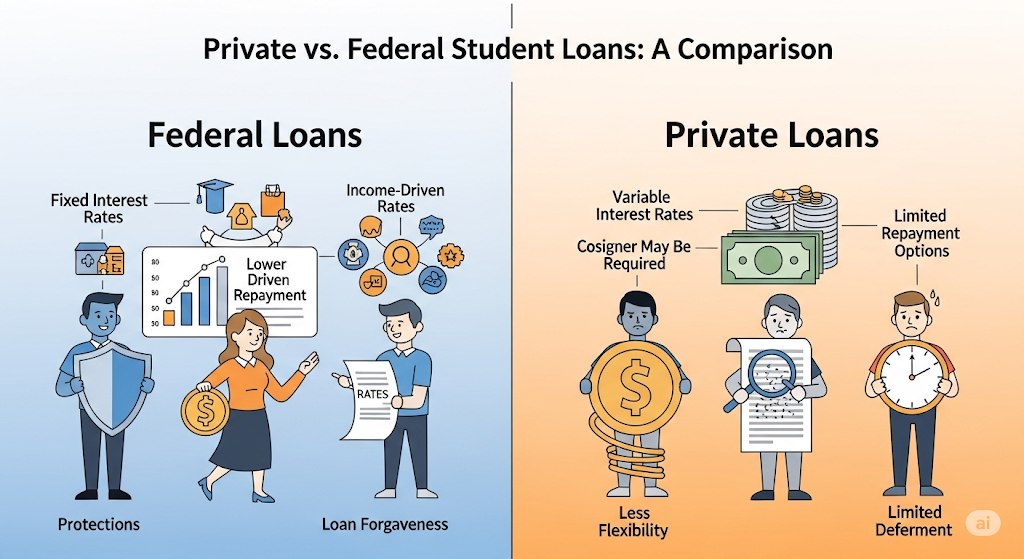
Federal Student Loans
- Offered by the U.S. Department of Education
- Fixed interest rates
- Income-driven repayment plans
- Generally unsecured
- Flexible deferment and forbearance options
Private Student Loans
- Offered by banks, credit unions, fintech lenders
- May require co-signers
- May check income or assets
- Still mostly unsecured
- Can have variable interest rates
Some private lenders may offer secured education loans, but it’s rare in the U.S. These are more common in countries like India or Singapore.
8. How Lenders Recover Money Without Collateral
Unsecured doesn’t mean “uncollectable.” Here’s how lenders enforce repayment:
- Credit Reporting: Delinquency and defaults are reported to credit bureaus.
- Wage Garnishment: Especially with federal loans, the government can garnish up to 15% of your paycheck.
- Tax Refund Seizure: The IRS may withhold your tax return to cover unpaid student loans.
- Collection Agencies: Aggressive recovery actions can be outsourced.
- Lawsuits: In some cases, lenders sue for repayment.
9. Are There Any Secured Student Loans?
In the U.S., secured student loans are extremely rare. However, here are exceptions:
- Home Equity Loan for Education: You use your home as collateral to finance your child’s education.
- Secured Private Loans in Other Countries: For example, in India, banks may offer student loans backed by property or FD (Fixed Deposits).
But mainstream U.S. student loans—whether federal or private—do not usually require collateral.
10. Impact of Unsecured Loans on Your Credit
Since student loans are unsecured, your credit report is the key enforcement mechanism.
- On-time payments help build credit history.
- Missed payments lower your FICO score.
- A default stays on your report for 7 years.
- Even closed loans with a good record boost credit standing.
11. Can You Get a Secured Student Loan in the USA?
Yes—but not through federal programs.
Some lenders may offer:
- Secured personal loans for education using CDs or savings accounts
- Parent PLUS loans that are secured by home equity (indirectly)
But these are not student loans in the traditional sense.
12. Pros and Cons of Unsecured Student Loans
✅ Pros
- No need for assets or collateral
- Easy access for students with no credit history
- Government protections and forgiveness programs
- Interest subsidies (for subsidized loans)
❌ Cons
- Higher interest compared to secured loans
- Risk of wage garnishment on default
- Very hard to discharge in bankruptcy
- Private lenders may demand co-signers
13. Student Loan Forgiveness & Repayment Plans
Since unsecured student loans can be burdensome, several programs help:
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF)
- Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Plans
- Teacher Loan Forgiveness
- Biden-Harris SAVE Plan (2024)
These reduce the repayment pressure—even though the loans are unsecured.
14. Tips to Manage Unsecured Student Loans
- Track Repayment Start Dates
Most loans give a grace period after graduation—know when your payments begin. - Set Up Auto-Pay
Many servicers offer 0.25% interest reduction for automatic payments. - Consolidate or Refinance (Carefully)
Consolidation makes management easier; refinancing may lower interest rates but removes federal protections. - Apply for IDR Plans Early
Base your payments on income if your job doesn’t support large monthly payments. - Never Ignore Your Loans
Communication is key—deferment and forbearance options can help during hardship.
15. Conclusion
So, are student loans secured or unsecured?
✅ Unsecured—in most cases.
While student loans do not require collateral, they come with serious consequences if neglected. Just because they’re unsecured doesn’t mean they’re low-risk for you as a borrower.
Understanding the legal and financial structure of your student loan—whether federal or private—empowers you to make better decisions about repayment, forgiveness, and financial planning.
16. FAQs
Q1: Can student loans be secured?
A: Not typically in the U.S. Some private loans may use collateral, but 99% are unsecured.
Q2: What happens if I default on an unsecured student loan?
A: You may face credit damage, wage garnishment, and tax refund seizure.
Q3: Do student loans affect your credit?
A: Yes. Positive repayment builds credit; defaults can severely damage it.
Q4: Can student loans be forgiven?
A: Federal loans may qualify for forgiveness via programs like PSLF and IDR after meeting certain criteria.
Q5: Are federal student loans secured?
A: No, they are unsecured and do not require collateral.
Q6: What is the difference between subsidized and unsubsidized loans?
A: Subsidized loans do not accrue interest while you’re in school; unsubsidized loans do.
Q7: Do you need a co-signer for unsecured student loans?
A: Not for federal loans. Private loans may require a co-signer if your credit/income is low.
Q8: Can private student loans be discharged in bankruptcy?
A: Rarely. It’s very difficult and requires proof of undue hardship.
Q9: Are student loans considered bad debt?
A: Not necessarily. If managed well, they can be a good investment in future earnings.
Q10: What is a secured loan example?
A: A mortgage is a classic secured loan—your home is collateral.




